概念
链表(Linked list)是一种线性表。由一系列节点对象组成,每个节点包含数据元素和一个指向下一个节点的引用,也就是说,各个节点通过“引用”相连接。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
class ListNode {
int elem;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int element) {
elem = element;
}
}
|
“引用记录了下一个节点的内存地址,通过它可以从当前节点访问到下一个节点。因此,链表的设计使得各个节点可以分散存储在内存各处,它们的内存地址无须连续。”
链表结构可以充分利用计算机内存空间,实现灵活的内存动态管理,同时,也失去了快速随机存取的优点(数组),同时增大了内存开销(存储下一个节点)。
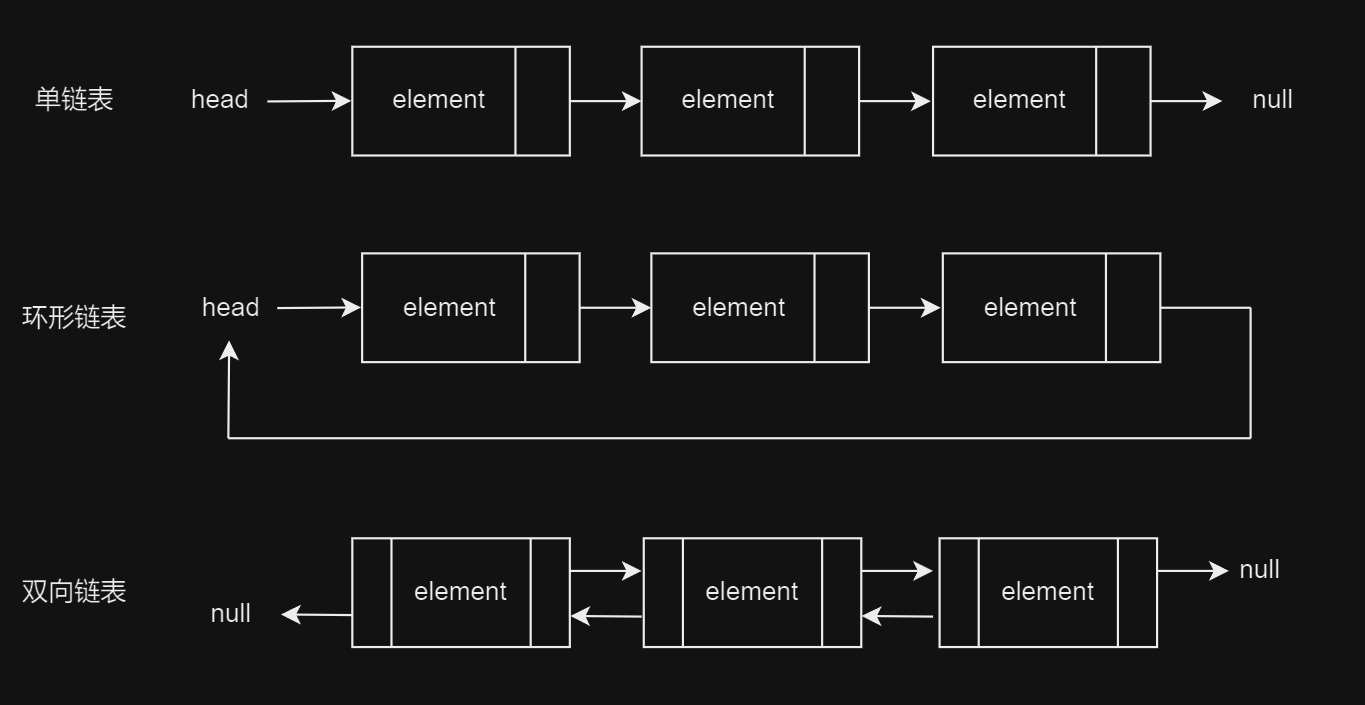
链表类型
常见链表类型有三种,分别是单链表,环形链表和双向链表。对比如下:
| 特性 |
单向链表 |
环形链表 |
双向链表 |
| 简介 |
简称单链表,是一种常规链表,其节点包含值和指向下一节点的引用两项数据,头节点指向第一个实际存储数据的节点,尾节点指向null。 |
首尾相接,将单链表的尾节点指向头节点就得到了一个环形链表。在环形链表中,任意节点都可以视为头节点。 |
与单链表相比,双向链表记录了两个方向的引用,也就是前驱结点prev和后继节点next,因此更加灵活,可以朝两个方向遍历链表。 |
| 节点结构 |
数据 + 下一节点的指针 |
数据 + 下一节点的指针 |
数据 + 下一节点的指针 + 前一节点的指针 |
| 遍历特点 |
单向遍历 |
循环遍历 |
双向遍历(前向和后向) |
头节点
在使用单链表的时候,我们通常会使用一个头节点(head)。
该头节点不存储数据,而是指向第一个实际存储数据的节点。
尾节点就是最后一个节点,该节点指向的下一个节点为null。
为什么需要头节点?
使用头节点,可以简化对链表的操作,提供一个固定的起点。如果没有头节点,我们在对链表进行插入、删除等操作时需要考虑处理第一个节点的特殊情况。头节点的存在使得链表的操作更加一致,使代码更加简洁和统一。
单链表的使用效果
下面,我们来编写一个单链表 LinkedList,实现之后可以这样使用它:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.addLast(10);
linkedList.addLast(20);
linkedList.addLast(30);
linkedList.addLast(40);
linkedList.addLast(50);
linkedList.addLast(60);
System.out.println("(1) 初始化后,当前链表为:" + linkedList.printList());
System.out.println("(2) 链表的大小:" + linkedList.size());
linkedList.add(1, 15);
System.out.println("(3) 在索引为1的位置插入元素15后,链表:" + linkedList.printList());
linkedList.addFirst(100);
System.out.println("(4) 在链表的头部添加一个元素100,链表:" + linkedList.printList());
System.out.println("(5) 判断链表是否包含元素15:" + linkedList.contains(15));
linkedList.set(5, 15);
System.out.println("(6) 将链表中索引为5的元素修改值为15,链表:" + linkedList.printList());
linkedList.remove(1);
System.out.println("(7) 将链表中索引为1的元素移除,链表:" + linkedList.printList());
linkedList.removeElement(50);
System.out.println("(8) 删除值为50的节点后,链表:" + linkedList.printList());
System.out.println("(9) 链表中索引为3的节点的值为:" + linkedList.get(3));
System.out.println("(10) 链表中第一次出现值为15的节点,其索引为:" + linkedList.indexOf(15));
System.out.println("(11) 链表中最后一次出现值为15的节点,其索引为:" + linkedList.lastIndexOf(15));
}
}
|
运行结果:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| (1) 初始化后,当前链表为:[10 → 20 → 30 → 40 → 50 → 60]
(2) 链表的大小:6
(3) 在索引为1的位置插入元素15后,链表:[10 → 15 → 20 → 30 → 40 → 50 → 60]
(4) 在链表的头部添加一个元素100,链表:[100 → 10 → 15 → 20 → 30 → 40 → 50 → 60]
(5) 判断链表是否包含元素15:true
(6) 将链表中索引为5的元素修改值为15,链表:[100 → 10 → 15 → 20 → 30 → 15 → 50 → 60]
(7) 将链表中索引为1的元素移除,链表:[100 → 15 → 20 → 30 → 15 → 50 → 60]
(8) 删除值为50的节点后,链表:[100 → 15 → 20 → 30 → 15 → 60]
(9) 链表中索引为3的节点的值为:30
(10) 链表中第一次出现值为15的节点,其索引为:1
(11) 链表中最后一次出现值为15的节点,其索引为:4
|
实现一个单链表

Node
在链表中,其组成元素都是节点(Node)对象。并且每个节点都包含两项数据:
- 节点的“值”(
elem)
- 指向下一个节点的“引用”(
next)
我们来写一下这个Node类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
|
public class Node {
private int elem;
private Node next;
public Node(int element, Node next) {
this.elem = element;
this.next = next;
}
public Node() {
this(0, null);
}
public void setElem(int element) {
this.elem = element;
}
public int getElem() {
return this.elem;
}
public void setNext(Node next) {
this.next = next;
}
public Node getNext() {
return this.next;
}
}
|
LinkedList
这里我们定义一个类,用于表示一个链表类。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public class LinkedList {
private Node head;
public LinkedList() {
this.head = new Node();
}
}
|
这样,我们就成功地初始化了一个单链表,可以在这个基础上进行后续的节点插入、删除等操作。
size
size() 方法用于获取链表的大小,即链表中包含的元素数量。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public int size() {
int count = 0;
Node current = head.getNext();
while (current != null) {
count++;
current = current.getNext();
}
return count;
}
|
isEmpty
判断链表是否为空,可以有两种策略:
- 策略一:使用
size()方法,判断链表存储的元素数量是否为0。
- 策略二:判断头节点的指针域是否为
null。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public boolean isEmpty() {
return head.getNext() == null;
}
|
clear
clear()方法用于清空链表,移除所有节点。实际就是将头节点的下一个节点设为null。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public void clear() {
head.setNext(null);
}
|
contains
contains(int element)方法用于判断链表是否含有指定元素element
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public boolean contains(int element) {
Node current = head.getNext();
while (current != null) {
if (current.getElem() == element) {
return true;
}
current = current.getNext();
}
return false;
}
|
set
set(int index, int element)方法用于设置链表中指定位置的元素值,并且返回原元素的值。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public int set(int index, int element) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {
if (index < 0 || index >= size()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("指定位置超出链表范围");
}
Node current = head.getNext();
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.getNext();
}
int oldValue = current.getElem();
current.setElem(element);
return oldValue;
}
|
printList
printList()方法用于打印链表。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
public String printList() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
result.append("[");
Node current = head.getNext();
while (current != null) {
result.append(current.getElem());
if (current.getNext() != null) {
result.append(" → ");
}
current = current.getNext();
}
result.append("]");
return result.toString();
}
|
插入元素
add
add(index, element)方法用于向在指定位置插入新元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public void add(int index, int element) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {
Node newNode = new Node(element, null);
if (index < 0 || index > size()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("插入位置超出链表范围");
}
Node current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.getNext();
}
newNode.setNext(current.getNext());
current.setNext(newNode);
}
|
Node current = head; 用于初始化一个临时节点(current),并将其设置为链表头节点(head),从头节点开始遍历链表。循环的次数为插入位置(index),每次迭代将current移动到下一个节点,最终将current移动到插入位置的前一个节点。
最后两行代码,用于将新节点的下一个节点设置为当前节点的下一个节点,然后将当前节点的下一个节点设置为新节点。这样就成功地在指定位置插入了新节点。
addLast
addLast(int element)方法,用于向链表的尾部添加一个新的元素,插入的新元素总是位于链表的末尾(也就是指针域为null的节点),我们称为尾插法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public void addLast(int element) {
Node node = new Node(element, null);
Node tail = head;
while (tail.getNext() != null) {
tail = tail.getNext();
}
tail.setNext(node);
}
|
addFirst
addFirst()方法用于向链表的头部添加一个新的元素,插入的新元素总是位于链表的头部(也就是头节点指向的节点),我们称之为头插法。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public void addFirst(int element) {
Node node = new Node(element, null);
node.setNext(head.getNext());
head.setNext(node);
}
|
可以看到,在链表头部插入元素的步骤如下:
- 根据新元素的值,构建一枚新节点
- 将新节点指针域置为原先链表中头节点指向的节点
- 最后,将头节点指向新节点
移除元素
remove
remove(int index)方法用于删除链表中指定位置index的元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public int remove(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {
if (index < 0 || index >= size()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("删除位置超出链表范围");
}
Node current = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.getNext();
}
Node removedNode = current.getNext();
current.setNext(removedNode.getNext());
return removedNode.getElem();
}
|
removeElement
removeElement(int element)方法用于删除链表中第一个出现的指定元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public boolean removeElement(int element) {
Node current = head;
while (current.getNext() != null && current.getNext().getElem() != element) {
current = current.getNext();
}
if (current.getNext() != null) {
current.setNext(current.getNext().getNext());
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
|
removeFirst
removeFirst()方法用于删除并返回链表中的第一个元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public int removeFirst() throws NoSuchElementException {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("链表为空");
}
Node firstNode = head.getNext();
head.setNext(firstNode.getNext());
return firstNode.getElem();
}
|
removeLast
removeLast()方法用于删除并返回链表中的最后一个元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public int removeLast() throws NoSuchElementException {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("链表为空");
}
Node secondLastNode = head;
while (secondLastNode.getNext().getNext() != null) {
secondLastNode = secondLastNode.getNext();
}
Node lastNode = secondLastNode.getNext();
secondLastNode.setNext(null);
return lastNode.getElem();
}
|
获取元素
get
get(int index)方法用于返回链表中指定位置的元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public int get(int index) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {
if (index < 0 || index >= size()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("指定位置超出链表范围");
}
Node current = head.getNext();
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) {
current = current.getNext();
}
return current.getElem();
}
|
getFirst
getFirst()方法用于获取链表中的第一个元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public int getFirst() throws NoSuchElementException {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("链表为空");
}
Node firstNode = head.getNext();
return firstNode.getElem();
}
|
getLast
getLast()方法,用于获取尾部元素。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public int getLast() throws NoSuchElementException {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("链表为空");
}
Node lastNode = head.getNext();
while (lastNode.getNext() != null) {
lastNode = lastNode.getNext();
}
return lastNode.getElem();
}
|
indexOf
indexOf(int element)方法用于查找链表中指定元素从前往后第一次出现的索引。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
public int indexOf(int element) {
int index = -1;
Node current = head.getNext();
int currentIndex = 0;
while (current != null) {
if (current.getElem() == element) {
index = currentIndex;
break;
}
current = current.getNext();
currentIndex++;
}
return index;
}
|
lastIndexOf
lastIndexOf(int element)方法用于查找链表中指定元素最后一次出现的索引。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
public int lastIndexOf(int element) {
int lastIndex = -1;
Node current = head.getNext();
int currentIndex = 0;
while (current != null) {
if (current.getElem() == element) {
lastIndex = currentIndex;
}
current = current.getNext();
currentIndex++;
}
return lastIndex;
}
|
数组 VS 链表
| 特性 |
数组 |
链表 |
| 存储方式 |
连续的内存块 |
分散的节点 |
| 访问元素 |
O(1) |
O(n) |
| 插入元素 |
O(n) |
O(1) |
| 删除元素 |
O(n) |
O(1) |
| 大小变化 |
固定,长度不可变 |
动态,可灵活扩展 |
| 内存使用 |
较少,预先分配空间 |
较多,动态分配空间 |






